2024铝合金形变热处理试验分析
摘 要
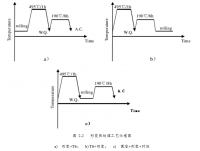
本文以 2024 铝合金形变热处理试验分析,采用形变工艺与热处理相结合的方法,设计了 12 种形变热处理工艺,采用电子背散射衍射、透射电镜、维式硬度、、圆环开口法等多种手段系统研究了 2024 铝合金组织演化与性能之间的相关关系,并筛选出了最佳的形变热处理工艺 。
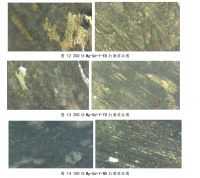
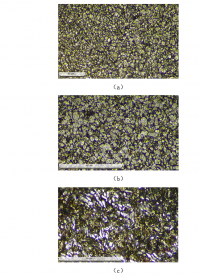
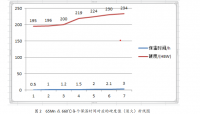
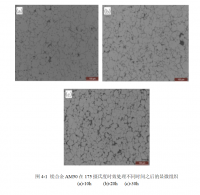
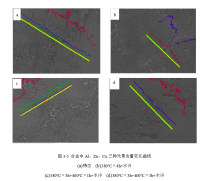
研究了不同形变量对 2024 铝合金组织和性能的影响。随着表面形变强化处理的形变量的增加,原始挤压成型棒材表面晶粒细化,经历了由挤压方向长轴亚晶粒到等轴亚晶粒,再到滚压方向长轴亚晶粒的转变。织构由挤压成型产生的<111>纤维织构,演变为<110>纤维织构。位错密度增加,产生大量滑移带。表面硬化层深度随形变量增加略有减小,其中以单边形变量 0.8mm 的工艺最佳,表面硬度最高达到 91MPa,提高了 34%。四种形变量下的硬化层深度均可达到 2.5mm 左右。
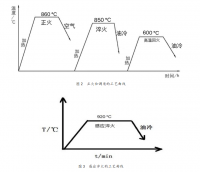
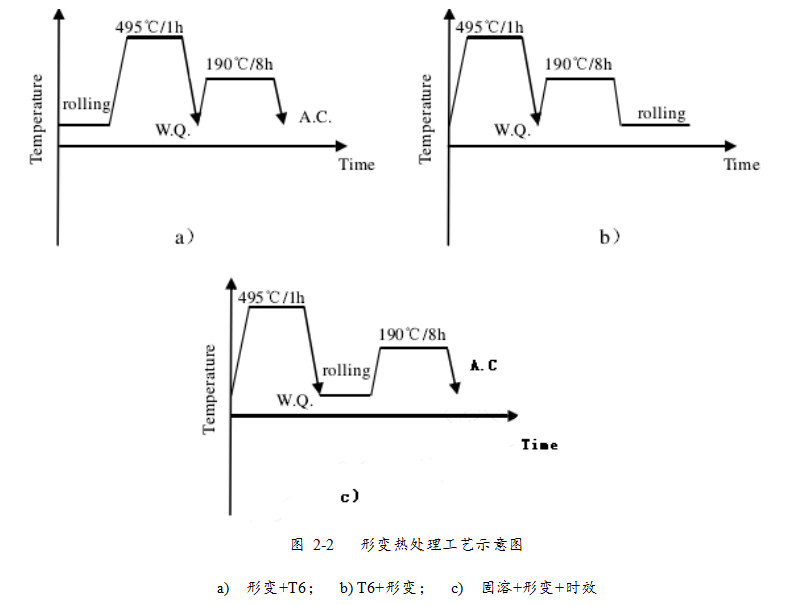
研究了形变对 2024 铝合金时效行为的影响。采用形变+固溶+时效(R+T6)、固溶+时效+形变(T6+R)、固溶+形变+时效(Q+R+A)三种不同形变热处理工艺。发现形变可以促进 2024 铝合金的中间相 S′在低温的析出。形变产生的高密度位错为 S′的析出提供形核场所,使得 S′相细小弥散,数量增加,强化效果显著。其中以Q+R+A工艺强化效果最优,表面硬化层深度 1.5mm 内的硬度值均达到 108MPa,比未进行形变处理时提高 20%。形变热处理工艺能够使 2024 铝合金棒材的摩擦系数减小,磨损率降低,耐磨性提高。其中以 Q+R+A 工艺对耐磨性的提高幅度最大,磨损率最低,在 200g 载荷下,摩擦系数为 0.378。
2024 铝合金径向的圆环开口测试表明,表面形变处理会引入大量宏观残余应力,降低材料的尺寸稳定性,经过 T6 处理后合金尺寸稳定性有所提高,再进行冷热循环处理,合金尺寸稳定性能进一步提高。其中尺寸稳定性能较优的工艺为Q+R+A+TCC 工艺。根据本文的研究结果,表面强化效果最佳的形变热处理工艺为 Q+R+A+TCC工艺。
关键词:2024 铝合金棒材;表面形变强化;形变热处理;尺寸稳定性
Abstract
The paper mainly aims experimental analysis on 2024 Aluminum Alloy thermomechanical treatment . Deformation was adopted combined with heat treatment process and 12 kinds of thermomechanical processes were designed. EBSD, TEM, Vickers hardness, friction and wear test, ring opening test and other methods were applied to investigate the relationship between the evolution of the microstructure and the mechanical properties of the 2024 aluminum. The optimal thermomechanical process was obtained finally.
The effect of different deformations on the microstructure and properties of 2024 aluminum alloy. With the increase of the deformation of the surface strain strengthening, the surface grain size of the original extruded rods get refined which leads to the transition fromt the axis subgrains of the extrusion direction to the axis subgrains of the rolling direction. Textures changes from muti-component <111>turns to <100>. The dislocation density increases and leads to the formation of slip bands. The thickness of the surface hardened layer decreases with the increase of the deformation. The process with the unilateral deformation of 0.8mm is the optimal. The surface hardness reaches 91MPa that is 34% higher than that of the untreated one. The thickness of the hardened layer under four kinds of deformations could reach about 2.5mm.
The effect of deformation on aging behavior of 2024 aluminum alloy was studied. Rolling-quenching-aging(R+T6), quenching-aging-rollin(T6+R),quenching-rolling- aging(Q+R+A) were carried out. It is found that deformation could promote the precipitation of the S′ phase in 2024 aluminum alloy at lower temperature. Dislocations generated from the deformation could provide nucleation sites for the precipitation of the S′ phase, which makes the size of the S′ phase precipitated during the aging process small and dispersive and increase the number at the same time. Therefore, the deformation strengthening before aging could make a more significant strengthening effect. By contrast, Q+R+A process gives the best strengthening effect. The hardness of the hardened layer within 1.5mm reaches 108Mpa, which improves 20% compared with that of the untreated specimen. The friction coefficients and wear rates of 2024 aluminum alloy bars could be reduced and the wear resistance could be improved after thermomechanical process. The Q+R+A process gives the optimal wear resistance. The friction coefficient decreases to 0.378 under the load of 200g and the wear rates are also
the lowest among different loads.
The radial ring opening test shows that surface deformation process would introduce large number of macroscopic residual stress, reducing the dimensional stability of the material. The dimensional stability of the alloy improves after T6 process.A follow-up thermal cycling treatment could further improve the dimensional stability of the alloy. The process that gives the alloy best dimensional stability is Q+R+A+TCC. According the results discussed in this paper, the process that has the best surface deformation strengthening effect on the alloy is Q+R+A.
Keywords::2024 aluminum alloy bar,surface deformation strengthening, thermomechanical treatment, dimensional stability
目 录
第一章 绪论 ------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9
1.1引言 ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 9
1.2 铝合金的发展及研究现状 ------------------------------------------------ 9
1.3 2xxx铝合金热处理工艺研究 -------------------------------------------- 15
1.4 变形铝合金的分类及应用 ----------------------------------------------- 18
1.5 热处理工艺的主要作用 -------------------------------------------------- 18
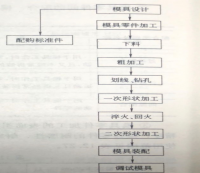
1.5.1 热处理工序在零件制造工艺流程中的位置 ------------------------ 19
1.5.2不同材料的热处理方式 ------------------------------------------------- 19
1.5.3热处理质量检验的特点 ------------------------------------------------- 20
1.5.4热处理工艺实施过程的坏境特点 ------------------------------------- 20
1.5.5 热处理工艺性及其影响因素 ------------------------------------------ 20
1.6 本论文研究的意义和内容 ----------------------------------------------- 20
第二章 实验材料及方法 --------------------------------------------------------- 22
2.1 实验材料 -------------------------------------------------------------------- 22
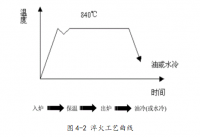
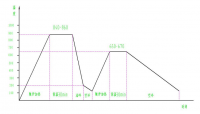
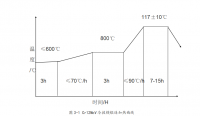
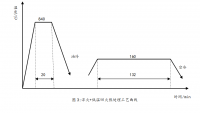
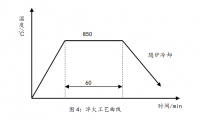
2.2 形变热处理工艺规程 ----------------------------------------------------- 22
2.3 试验方法 -------------------------------------------------------------------- 25
2.3.1 显微组织观察 ------------------------------------------------------------ 25
2.3.2 电子背散射衍射分析 -------------------------------------------------- 26
2.3.3 圆环开口尺寸测试 ----------------------------------------------------- 26
2.3.4 维式硬度测试 ---------------------------------------------------------- 29
第三章 实验结果与分析 -------------------------------------------------------- 30
3.1 引言 ------------------------------------------------------------------------ 30
3.2 铝合金实验结果 ----------------------------------------------------------- 30
3.2.1 形变量不同对晶粒取向的影响 ------------------------------------- 30
3.3 形变量不同对2024铝合金硬度的影 ----------------------------------- 32
3.3.1 形变量不同对表面硬化层深度的影响 ------------------------------ 32
3.3.2 变形量不同对硬度的影响 --------------------------------------------- 33
3.4 形变对 2024 铝合金尺寸稳定性的影响-------------------------------- 34
本章小结 --------------------------------------------------------------------------- 35
结论 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 37
参考文献---------------------------------------------------------------------------- 38
致谢 --------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 39
第一章 绪 论
1.1引言
铝元素作为地壳中含量丰富(金属元素中总储量排第二)的金属元素,19 世
纪末,开始在工程应用领域备受关注。从高纯铝到最复杂的合金,其物理性能和机械性能分布范围广泛,这种多功能性是非常具有吸引力和竞争力的,目前为止,已经有三百多种合金成分得到广泛的认可与应用。铝合金的优异性能,使其应用于包括包装、交通、建筑、航空航天、石油在内的多个行业和领域。
参考文献
[1] Ashutosh Sharma, Sanjeev Das. Study of age hardening behavior of Al-4.5wtCu/zircons and Composite in different quenching media-A comparative Study. Material Design, 2009, 202(30): 3900-390
[2] WarrenA.5., Developments and Challenges for Aluminum-A Boeing Perspective, the 9th-international conference on aluminum alloys, 2004, Australia.
[3] 朱宝宏. 2139 铝合金热处理工艺及组织性能研究[D]。北京有色金属研究总院博士学位论文, 2011
[4] 潘志军,黎文献等.高强铝合金研究现状与展望[J] .铝加工,2000 24(4) :39-41
[5] 刘静安, 谢水生. 铝合金材料的应用与技术开发[M]. 北京:冶金工业出版社,2002
[6] 徐崇义,李念奎.2×××系铝合金强韧化的研究与发展. 《轻合金加工技术》 2005 (18):13-17
[7] 王祝堂, 田荣璋. 铝合金及其加工手册[M]. 长沙:中南工业大学出版社,1989
[8] 刘成,罗兵辉. 2024 铝合金的均匀化热处理研究.铝加工,2010( 4 ):8-14
[9] 刘晓涛,董杰,崔建忠. 高强铝合金均匀化热处理.中国有色金属学报, 2003(08):909-913
[10] S.C.Wang, M.J.Starink, Review of precipitation in Al-Cu-Mg-(Li) alloys[J], Int. Mater Rev,2005,50:193-215
[11] Mukhopadhyay A K, Rama R V. Characterization of S(Al2CuMg) phase particles present in as-cast and annealed Al-Cu-Mg(-Li)-Ag alloys. Materials Science and Engineering A,1999,268:8-14
[12] Charles K.S. Moy, Matthias Weissd, Junhai Xia, ect. Influence of heat treatment on the microstructure, texture and formability of 2024 aluminum alloy. Materials Science and Engineering A 552 (2012) 48– 60
[13] O. Beffort, C. Solenthaler, M.O. Speidel. Improvement of strength and fracture toughness of a spray-deposited Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Mn-Ti-Zr alloy by optimized heat treatments and thermomechanical treatments. Materials Science and Engineering Al 91 (1995) 113-l 20
[14] 杨平.电子背散射衍射技术及其应用[M].北京:冶金工业出版社,2007.