基于PLC的中小型立体仓库设计
摘要:传统仓库的存在成了生产力扩大的一个障碍。为了提高仓库的利用率,实现仓库的最大利用率,新一代立体仓库的建立是必不可少的。高达5米以上的机械化仓库,运用可编程控制系统,实现仓库的自动化成为了一种趋势。而就是通过对软件以及机械的综合运用来设计一款中小型立体仓库。解决传统仓库所带来的低利用率、高浪费率。通过自动化的控制不仅可以减少货物的进出库时间,同时又大大减少了人力成本。无形中解决了传统仓库在高成本人力地区的花费,实在是一举两得。
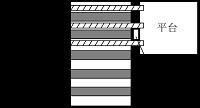
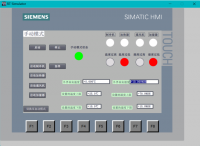
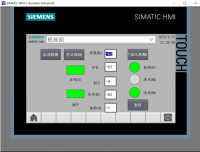
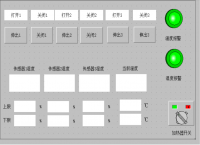
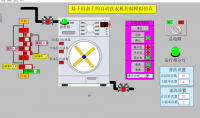
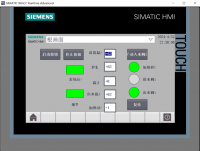
立体仓库是由PLC控制的新型存储模式,人在这里面只是起到一个监控作用,当有货物需要进出仓库时,可以有两种模式进行操作。第一种,通过系统所有的扫描器扫描货箱上的条形码进行自主定位,从而控制整个仓库的运转。第二种,人为控制,控制系统中有手动操作,需要人本身进行定位,当然根据具体情况,系统也可以提供手动进出库,全程由人来控制。
关键词:生产力;利用率;立体仓库;机械化;可编程控制系统;自动化
Small and medium-sized warehouse design based on PLC
Abstract: The existence of the traditional warehouse has become an obstacle to productivity to expand. In order to improve the utilization of warehouse to achieve maximum utilization of the warehouse, a new generation of the establishment of the stereoscopic warehouse is indispensable. Up to 5 meters above the mechanization of the warehouse, using the programmable control system, realize the warehouse automation has become a trend. And I think I can be through the integrated use of the software and the mechanical design a small and medium-sized warehouse. The traditional warehouse caused by the low utilization and high rate of waste. Through automated control can not only reduce the outbound time of goods, and greatly reduce the labor costs at the same time. Virtually solved the traditional warehouse in high cost of manpower cost, it is kill two birds with one stone.
Stereoscopic warehouse is a new kind of storage model is controlled by PLC, people just have a monitoring effect on the inside, when has the goods need to pass in and out warehouse, we can have two modes of operation. First, through the system all the scanner scans the bar code on the crate positioning independently, so as to control the whole warehouse operation. Second, artificial control, manual operation control system, need people to locate itself, of course according to the specific situation, system can also provide manual and outbound, all to be controlled by man.
Keywords: Productivity; Utilization; Stereoscopic warehouse; Mechanization; Programmable control system; automation
目录
摘要. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .I
第一章 绪论. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.1立体仓库的历史及现状. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.2立体仓库的发展方向. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
1.3立体仓库的重要意义. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
第二章 硬件结构设计. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
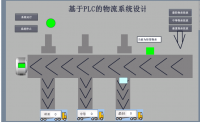
2.1立体仓库的结构. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
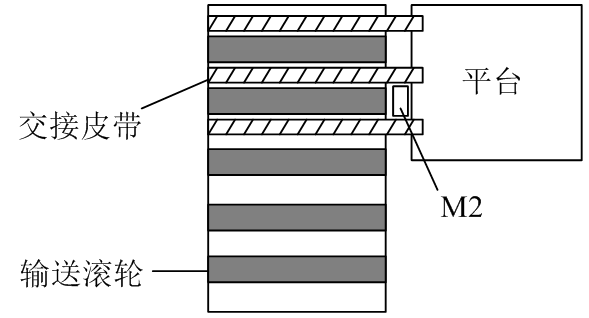
2.2输送设备. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
2.3升降设备. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
2.4安全保障. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .4
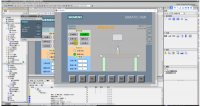
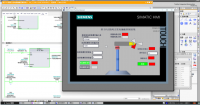
第三章 PLC程序的设计. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
3.1PLC的选型 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .6
3.2输送程序. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .8
3.3传递程序. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
3.4提取货物程序. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
第四章 整体设计调试. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
4.1传感器的选用 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .11
4.2主电路设计. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .13
第五章 结论. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .14
小结与致谢. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15
参考文献. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .16
附录. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .17
参考文献
[1] 吴宗泽.机械设计师手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2002
[2] 王太辰.中国机械设计大典[M].南昌:江西科技出版社,2002
[3] 彭商贤,赵臣,张启先.试论国内外机器人机械学的发展趋向[M].1991.13:48-53
[4] 吴建强.可编程控制器原理及其应用[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,1998
[5] 汪晓光,孙晓瑛.可编程控制器原理及应用[M].机械工业出版社,2001
[6] 刘彬,杜金翔.关于建立PLC立体教学实验新体系的探讨[M].实验技术与管理[M].2005,08:25-30
[7] 俞国亮.PLC原理与应用[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2005:259-268
[8] 史宜巧.PLC技术及应用[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2009:177-184
[9] 廖常初.PLC编程及应用[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2004
[10] 周亚军,张卫.电气控制与PLC原理及应用[M].西安:西安电子科技大学出版社,2010
[11] 郁汉琪.可编程控制器原理与应用[M].北京:中国电力出版社,2008
[12] 宋伯生.PLC编程理论·算法及技巧[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2005
[13] 周永志,袁少帅.PLC实现机器人的自动控制[M].上海:上海科学技术文献出版社,2010
[14] 彭秀英,陈亚,胡园.基于PLC控制的气动模拟测量系统的研究设计[M].西安:电子工业出版社,2010
[15] 吴旗.传感器及应用[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2002
[16] 许志军.工业控制组态软件及应用[M].北京:机械工业出版社.2005:192-198
[17] 廖常初.可编程控制器的编程方法与工业应用[M].重庆:重庆大学出版社.2001:26-37
[18] 张凤珊.电器控制及可编程序控制器[M].北京:中国轻工业出版社.1999:62-79
[19] 吴建强.可编程控制器原理及其应用[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社.1998:12-60
[20] 林小峰.可编程序控制器及应用[M].北京:高等教育出版社.1991:17-26
[21][苏]A.A.斯麦霍夫.自动化仓库[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2001
[22]虞和谦.高层货架仓库讲座[J].物流技术.1997
[23]蔡传杰.自动仓储控制系统[M].机械技术(台湾). 2001.(3).
[24]丁晓红.自动化立体仓库的实时监控系统[M].起重运输机械.1996 (12)
[25]常发亮,李幕兰,林连序.自动化立体仓库PLC 控制系统[J].电器自动化.1995 (4), 45-47
http://www.bysj1.com/ http://www.bysj1.com/html/4774.html http://www.bysj1.com/html/3599.html