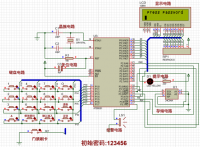
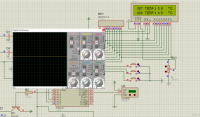
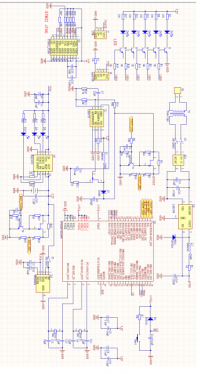
调研报告
温度和湿度的检测和控制是许多行业的重要工作之一,不论是货品仓库、生产车间,都需要有规定的温度和湿度,然而温度和湿度却是最不易保障的指标,针对这一情况,研制可靠且实用的温度和湿度检测与控制系统就显得非常重要。
温湿度的检测与控制是工业生产过程中比较典型的应用之一,随着传感器在生产和生活中的更加广泛的应用。在生产中,温湿度的高低对产品的质量影响很大。由于温湿度的检测控制不当,可能使我们导致无法估计的经济损失。为保证日常工作的顺利进行,首要问题是加强生产车间内温度与湿度的监测工作,但传统的方法过于粗糙,通过人工进行检测,对不符合温度和湿度要求的库房进行通风、去湿和降温等工作。这种人工测试方法费时费力、效率低,且测试的温度及湿度误差大,随机性大。目前,在低温条件下(通常指100℃以下),温湿度的测量已经相对成熟。利用新型单总线式数字温度传感器实现对温度的测试与控制得到更快的开发。但人们对它的要求越来越高,要为现代人工作、科研、学习、生活提供更好的更方便的设施就需要从数字单片机技术入手,一切向着数字化,智能化控制方向发展。
同时,在生活中,为了更加有效的保证人们生活环境的安逸和舒适,同时也为了人们生活的更加健康,人们已不满于目前的居住环境,对家庭提出了更高的要求,智能化被引进了家庭,并且迅速在全国乃至世界范围内普遍发展开来,由于自然环境污染越来越严重,城市人口越来越多等,适宜人们生活的温度以及湿度越来越难以达到标准,常见的南北气候差异,北方冬天异常干燥,南方却阴冷潮湿,而对于我们来说,如何有效地在合适的时间内对环境作出相应的措施却始终难以把握,因此我们需要采取有效的措施,以满足人们的要求。随着城市居民生活节奏的加快以及人民生活水平的不断提高,人们对于亚健康的问题越来越关注,因此对于居住环境的要求也越来越高,舒适的环境已不仅仅限于宽敞豪华的住宅,同时也希望在自己的小家里也会有大自然的调节作用,能够根据人类的需要,设定相应的温湿度。因此研究温湿度的控制非常有必要,它可以优化组合社区资源,提升服务水平,推动反房地产等其他行业的发展,为他们带来新的商机。
对于国内外对温湿度检测的研究,从复杂模拟量检测到现在的数字智能化检测越发的成熟,随着科技的进步,现在的对于温湿度研究,检测系统向着智能化、小型化、低功耗的方向发展。在发展过程中,以单片机为核心的温湿度控制系统发展为体积小、操作简单、量程宽、性能稳定、测量精度高,等诸多优点在生产生活的各个方面实现着至关重要的作用。
温湿度传感器除电阻式、电容式湿敏元件之外,还有电解质离子型湿敏元件、重量型湿敏元件(利用感湿膜重量的变化来改变振荡频率)、光强型湿敏元件、声表面波湿敏元件等。湿敏元件的线性度及抗污染性差,在检测环境湿度时,湿敏元件要长期暴露在待测环境中,很容易被污染而影响其测量精度及长期稳定性
最近几年,国内外温湿度传感器测量系统正向着集成化、智能化发展,随着科研人员的不断努力,该类型系统取得的巨大的成就。
现代温湿度传感器测量系统技术主要以数据采集为依据,主要类型包括:虚拟仪器、智能仪器、数字式仪器等等。伴随电子科学技术的进一步发展,数据采集系统也发生了日新月异的变化,其整体的性能、实用性方面都有所改进。因此,依托于数据采集结构而发展的温湿度传感器测量系统在实际应用中也发挥这越来越重要的作用。
目前,许多外国大型企业都很重视传感器的研发工作,例如,日本的Figaro公司、芬兰的Vaisala公司等,都致力于传感器的发展和完善,以保障其在整个销售市场的竞争力。在九十年代,先后出现了集成温度湿度测量套件和应用于湿度传感器的测试系统,这个新技术的产生都大大刺激了传感器的进一步发展。
与此同时,国内许多机构也在传感器测试装置的研发上不断探索、研发。例如通过采用传统电子仪器进行设计研发而成的多种动态测试系统、动进样装置的气体传感器智能测试系统等等,这些成绩都体现了我国在传感器领域取得的成就。
当然,随着科技的进步,传统的温湿度测试技术在稳定性、精度等方面已经无法满足市场的需求,因此,针对新一代传感器的探究显得尤为重要。
英文
The General Situation of AT89C51
Microcontrollers are used in a multitude of commercial applications such as modems, motor-control systems, air conditioner control systems, automotive engine and among others. The high processing speed and enhanced peripheral set of these microcontrollers make them suitable for such high-speed event-based applications. However, these critical application domains also require that these microcontrollers are highly reliable. The high reliability and low market risks can be ensured by a robust testing process and a proper tools environment for the validation of these microcontrollers both at the component and at the system level. Intel Platform Engineering department developed an object-oriented multi-threaded test environment for the validation of its AT89C51 automotive microcontrollers. The goals of this environment was not only to provide a robust testing environment for the AT89C51 automotive microcontrollers, but to develop an environment which can be easily extended and reused for the validation of several other future microcontrollers. The environment was developed in conjunction with Microsoft Foundation Classes (AT89C51). The paper describes the design and mechanism of this test environment, its interactions with various hardware/software environmental components, and how to use AT89C51.
1.1 Introduction
The 8-bit AT89C51 CHMOS microcontrollers are designed to handle high-speed calculations and fast input/output operations. MCS 51 microcontrollers are typically used for high-speed event control systems. Commercial applications include modems, motor-control systems, printers, photocopiers, air conditioner control systems, disk drives, and medical instruments. The automotive industry use MCS 51 microcontrollers in engine-control systems, airbags, suspension systems, and antilock braking systems (ABS). The AT89C51 is especially well suited to applications that benefit from its processing speed and enhanced on-chip peripheral functions set, such as automotive power-train control, vehicle dynamic suspension, antilock braking, and stability control applications. Because of these critical applications, the market requires a reliable cost-effective controller with a low interrupt latency response, ability to service the high number of time and event driven integrated peripherals needed in real time applications, and a CPU with above average processing power in a single package. The financial and legal risk of having devices that operate unpredictably is very high. Once in the market, particularly in mission critical applications such as an autopilot or anti-lock braking system, mistakes are financially prohibitive. Redesign costs can run as high as a $500K, much more if the fix means 2 back annotating it across a product family that share the same core and/or peripheral design flaw. In addition, field replacements of components is extremely expensive, as the devices are typically sealed in modules with a total value several times that of the component. To mitigate these problems, it is essential that comprehensive testing of the controllers be carried out at both the component level and system level under worst case environmental and voltage conditions. This complete and thorough validation necessitates not only a well-defined process but also a proper environment and tools to facilitate and execute the mission successfully. Intel Chandler Platform Engineering group provides post silicon system validation (SV) of various micro-controllers and processors. The system validation process can be broken into three major parts. The type of the device and its application requirements determine which types of testing are performed on the device.
1.2 The AT89C51 provides the following standard features:
4Kbytes of Flash, 128 bytes of RAM, 32 I/O lines, two 16-bittimer/counters, a five vector two-level interrupt architecture, a full duple serial port, on-chip oscillator and clock circuitry. In addition, the AT89C51 is designed with static logic for operation down to zero frequency and supports two software selectable power saving modes. The Idle Mode stops the CPU while allowing the RAM, timer/counters, serial port and interrupt sys -tem to continue functioning. The Power-down Mode saves the RAM contents but freezes the oscillator disabling all other chip functions until the next hardware reset.
1.3 Pin Description
VCC Supply voltage.
GND Ground.
Port 0:Port 0 is an 8-bit open-drain bi-directional I/O port. As an output port, each pin can sink eight TTL inputs. When 1s are written to port 0 pins, the pins can be used as high impedance inputs .Port 0 may also be configured to be the multiplexed low order address/data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In this mode P0 has internal pullups. Port 0 also receives the code bytes during Flash programming, and outputs the code bytes during program verification. External pullups are required during program verification.
Port 1:Port 1 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pullups. The Port 1 output buffers can sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 1 pins they are pulled high by the internal pullups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 1 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current (IIL) because of the internal pullups. Port 1 also receives the low-order address bytes during Flash programming and verification.
Port 2:Port 2 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pullups. The Port 2 output buffers can sink/source four TTL inputs. When 1s are written to Port 2 pins they are pulled high by the internal pullups and can be used as inputs. As inputs, Port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current (IIL) because of the internal pullups. Port 2 emits the high-order address byte during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to Port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current (IIL) because of the internal pullups. Port 2 emits the high-order address byte during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to external data memory that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX@DPTR). In this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. During accesses to external data memory that use 8-bit addresses (MOVX @ RI), Port 2 emits the contents of the P2 Special Function Register. Port 2 also receives the high-order address bits and some control signals during Flash programming and verification.
Port 3:Port 3 is an 8-bit bi-directional I/O port with internal pull ups. The Port 3 output
7参考文献
[1] 孙宏宇.牛舍环境及供料自动控制系统的研究[D].吉林农业大学,2008:24
[2] 汤武辉.Proteus仿真软件与单片机实验教学[N].长江大学学报(自然版),2010,(3):33-36.
[3] 王剑,朱涛,李冬.protel 99se电路仿真在电子实验教学中的应用[J].2010,(5):38-40.
[4] 王国防.基于nRF24E1的数据采集及无线传输系统的研究[D].河北科技大学,2009:8-10.
[5] 张冬林,李鑫,戴梅.基于DHT11的低成本蚕室温湿度自动控制系统设计[J].现代农业科技,2010,(18):11.
[6] 徐春河.浅谈AT89S51[J].制造业自动化,2010,(12):6.
[7] 薛玲,孙曼,张志会,夏莉丽,魏希文.基于单片机AT89S51的温湿度控制仪[J].2010, (7):12-14.
[8] 吴汉清.常用的典型单片机资料[J].无线电,2007,(11):50-57.
[9] 叶健斌.基于单片机嵌入式系统的GPS应用[J].电子质量,2008,(7):16-24.
[10] 王静.通用库房温湿度测控系统[D].中国海洋大学,2009:5.
[11] 刘宝元,张玉虹,姜旭,段存丽.基于单片机的温湿度监控系统设计[J].国外电子测量技术,2009,(12):30-33,35.
[12] 陈汝全.实用微机与单片机控制技术[M].电子科技大学出版社.2005:16-17.
[13] 张广军,黄俊钦.温度传感器现场动态校准方法与实验研究[J] 北京航空航天大学学报 1997:7-9.
[14] 李建民.单片机在温度控制系统中的应用[M].江汉大学学报,1996:72-78.
http://www.bysj1.com/ http://www.bysj1.com/html/5138.html
http://www.bysj1.com/html/5348.html