几种纯金属熔体黏度试验方法与分析
摘要:
金属熔体的粘滞性是液态金属原子迁移的一种表现,是原子间结合力大小的反映,是熔体的重要物理性质之一。液态金属的粘度是对金属熔体结构十分敏感的性质,研究熔体粘度对于液态金属结构相关的基础科学和科技应用有非常重要的意义。熔体的粘度是反映熔体结构变化的敏感参数,但是对熔体激活能的相关研究还是比较薄弱的,特别是液相线之上关于激活能的相关信息比较少,而施加外界条件下的相关激活能的研究更是不多。
本文以Sn、Al、In、Bi等纯金属单质为研究对象,利用带水平磁场的高温熔体粘度仪,测量了不同熔体在不同磁场强度下的粘度,探讨了熔体的粘度与磁场强度以及自身结构之间的关系,以及纯金属单质熔体的粘滞激活能与其熔点之间的关系。
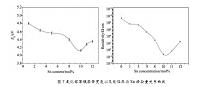
研究表明,纯金属熔体Sn、Al、In、Bi在分别在90Gs,420Gs,760Gs以及1000Gs水平磁场强度下的黏度遵循随着温度的升高而降低的规律,且Sn、Al、In、Bi熔体的黏度也随着磁场强度的增加而增大;金属在熔融状态下可以认为熔体是由金属阳离子与核外的自由电子构成。温度较高时,Sn、Al、In、Bi等纯金属熔体在相同过热温度条件下,In,Al熔体的粘度变化率远大于Sn, Bi熔体的变化率,这是因为Al, In熔体是“离子”熔体,因阳离子受洛伦兹力增加了粒子之间的摩擦,而Sn,Bi熔体因有非极性共价键不受洛伦兹力作用,即黏度的变化率更小;因此,Al, In熔体的的粘度增长率要大于Sn, Bi熔体,且Al熔体的温度高,磁场对其粘度影响大,所以粘度增加较多;
关键词:黏度;纯金属;熔体;激活能;高温熔体粘度仪
Experimental methods and analyses on viscosity of several pure metal melt
Abstract: The viscosity of molten metal is a kind of liquid metal atom migration, reflects the inter atomic bonding force, is one of the important physical properties of melt. Liquid metal viscosity is very sensitive to the properties of melt structure, has a very important significance to study the melt viscosity of liquid metal structure of basic science and technology. The viscosity of the melt is a sensitive parameter to reflect the change of the melt structure, but on the melt activation related research is still relatively weak, especially the liquidus on the relevant information about the activation energy is less, and applied research related to the activation energy of the external conditions are not much more.
In this paper, using Sn, Al, In, Bi and other pure metals as the research object, the use of high temperature melt viscosity instrument with the horizontal magnetic field, whose strength is 90Gs,420Gs,760Gs or 1000Gs, was measured under different magnetic field intensity of the melt viscosity, discusses the relationship between the viscosity and the strength of the magnetic field and the structure of the melt viscosity of pure metal melt, and the activation energy of pure relationship its melting point.
Research shows that, in the magnetic field under the conditions of pure metals, the melt viscosity decreases with the increase of temperature, and in accordance with the formula of Arrhenius; In the horizontal magnetic field conditions, the melt viscosity increased. Metal can be thought of as melt is composed of free electron metal cation and the nucleus in the molten state. When the temperature is high, the thermal motion of metal cations magnetic line cutting in a magnetic field, will be Lorenz, caused by the movement state change, resulting in the melt viscosity increased; at the same temperature, the higher the strength of the magnetic field, the viscosity of the melt is bigger, the pure aluminum melt viscosity increases. Because of the quality of aluminum atoms and small, completely into the aluminum ions in the melt, and melt tin secret inside contains a covalent bond, can not be completely into the metal cations, so that changes in the degree of change of tin secret melt viscosity of aluminum melt viscosity under no magnetic field; at the same time in a magnetic field, the viscous activation energy of metal melt is also larger.
Keywords: Pure metal melt; viscosity;; activation energy; High Temperature Melt Viscosity Meter
目录
第一章 绪论 1
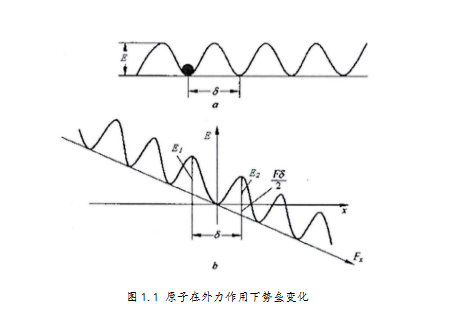
1.1 金属熔体的黏度 1
1.2 测量金属熔体黏度的方法 5
1.2.1 测量液态金属黏度的几种方法 5
1.2.2 决定熔体黏度的参数 7
1.2.3 影响液态金属熔体黏度及测量准确性的相关因素 8
1.3 金属熔体黏滞性的研究现状 9
1.3.1 纯金属熔体黏度与熔体物理性质的关系及研究现状 10
1.3.2 磁场条件下金属熔体粘滞性的研究现状 12
1.3.3 液态结构的研究现状 12
1.4 本课题的研究意义和内容 13
第二章 实验材料和方法 15
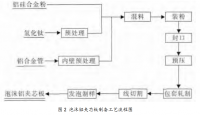
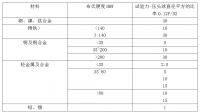
2.1 试验用料和加工办法 15
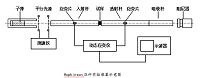
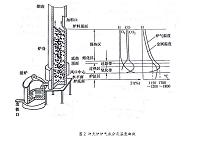
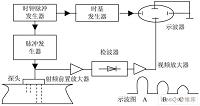
2.2 试验所用仪器以及测量基本原理 15
2.2.1 黏度仪主体 15
2.2.2 测量的基本原理 19
2.2.3 X射线衍射装置简介 20
第三章 试验结果与分析 22
3.1 纯金属熔体Cu、Sn的黏度 22
3.2 纯金属熔体Sn、Al、In、Bi在不同磁场强度下的黏度 23
3.3 Sn、Al、In、Bi等纯金属熔体的液态结构 26
3.4 Sn、Al、In、Bi等不同类型纯金属熔体在相同过热度下的黏度 29
3.5 纯金属熔体Sn、Al、In、Bi的激活能 31
3.6 多种纯金属熔体激活能与液相线的温度关系 31
3.7 纯金属熔体Al, In, Sn, Bi在磁场下的粘滞激活能 32
总结 34
参考文献 35
参考文献
[1] 陈惠钊,粘度测量,北京:国际两出版社,1994. 155-288
[2] 陈惠钊.粘度测量[M],北京:中国计量出版社,2003
[3] 张承甫,龚建森,黄杏蓉,王凯歌.液态金属的净化与变质[M],上海:上海科技出版社,1989, 21
[4] 陆坤权,物理,1997 26(1),23-25
[5] 下地光雄,液态金属,北京:科学出版社,1987,203-204
[6] 藤新营,闵光辉,材料科学与工艺,2001,9(4),383-385
[7] 杨志伊,王坤东.磁场中磁流体粘度测试系统的实现[J],机械工程材料,2003,27(5),22-25
[8] 汪复兴,金属物理,北京:科学出版社,1986,101-140
[9] 杨志伊,王坤东,机械工程材料,2003. 27(5). 22-25
[10] 程素娟.金属熔体原子团簇的微观热收缩现象「D]山东大学博士学位论文,2004年
[11] 孙民华,耿浩然,边秀房等.A1熔体粘度的突变点及与熔体微观结构的关系[J],金属学报.2000,36(11),1134-1138
http://www.bysj1.com/ http://www.bysj1.com/html/3115.html http://www.bysj1.com/html/2315.html