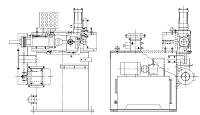
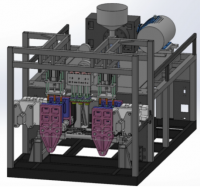
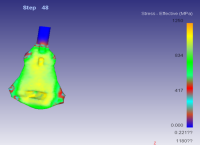
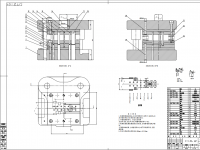
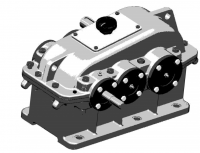
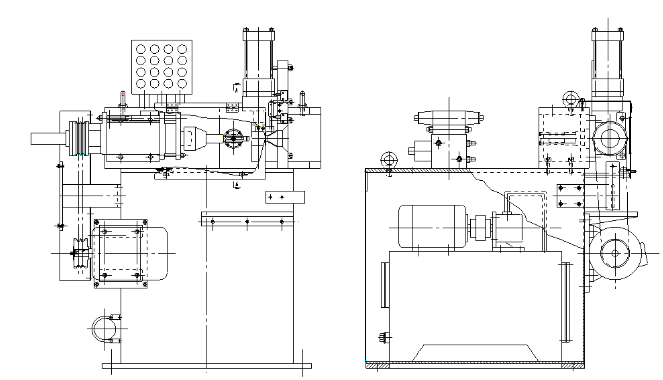
旋转式管端机结构设计
摘要:管端成型是国内所需空调设备的重要组成部分,专门从事制造管端成型的通用机床较少,而且其中大部分都是专用机床,生产效率高,不过灵活性方面小,处理不同的管件有一定的局限性。目前来看,国内胀管方法主要包括机械成型,管端偏心回转成型,利用NC工作机的管端成型和无模成型这四种方法。以经济性和结构为基本考虑,此设计的管端成型机的设计及胀管的方法是相对普遍常见,相对容易实现工作要求,原理简单,操作方便。该机床是一种通用机床,可以适应不同管件成型加工,在小批量单件生产时的手工管端成型的条件下,可以节省时间和生产消耗,提高单一的生产效率和生产消费,以满足产品零部件的需要。换热器使用的空调管管端成型机,即通过冲压或旋压的方式将铜铝管变细加工成所需的管端形状,后来用于空调器热交换器或汽车空调热交换器的管端连接。该机把铝管或铜管管端加工成杯状或喇叭状,适合大规模生产,此胀管方法能完成直径9.42X1.2、9X1.2、12.6X1.2、15.8X1.2、19.1X1.2mm的铝管或铜管,也可以满足其它材料配件。因为该机的工作周期短,经常运动的方向变化,让机器在交变应力下更明显,所以要高强度的工作机械零件。
关键词:管端成型机;胀形加工;专用机床
Structural design of Rotary tube transmitter
Abstract: tube end forming is an important part of the domestic air conditioning equipment required, specializes in the manufacture of pipe end forming of general purpose machine tools less, and most of them are special machines, high production efficiency, but flexibility in the small, dealing with different tube has some limitations. At present, internal tube methods include mechanical, eccentric Rotary tube end molding, use of NC machine of pipe end forming and freeform fabrication of these four methods. The economy and structure as the basic considerations, design of pipe end forming machine of this design and tube expanding technique is relatively common, relatively easy to implement work requirements, simple, easy to operate. The machine is a universal machine, can adapt to different pipe forming, in small batch production of pipe end forming by hand under the conditions, you can save time and cost, improve production efficiency and production of single consumption in order to meet the needs of product components. Use air conditioning tube heat exchanger tube end forming machines, namely by way of stamping or spinning of CU-Al pipe thinner processed into the desired shape of the pipe end, later used for heat exchanger of air conditioners or auto air conditioning pipe end connections of the heat exchanger. This machine is processed into aluminum pipe or copper pipe end Cup-shaped or Bell-like and suitable for mass production, this tube Expander method to finish diameter (9.42X1.2, (9X1.2, (12.6X1.2, (15.8X1.2, (19.1X1.2mm aluminum pipe or copper pipe or accessories of other materials. Because the machine's working cycle is short, often the direction of motion changes to machines in alternating stress is more obvious, so the intensity of the mechanical parts.
Key words: pipe end forming machine bulging processing machine
目录
第一章绪论···················································9
1.1旋转式管端机结构的背景······································9
1.2旋转式管端机结构的特点······································9
1.3旋转式管端机结构的研究内容··································9
第二章方案的确定·············································10
2.1管端成型的方法与原理········································10
2.2管端成型方法的选择确定······································10
2.3管端成型机构的组成··········································10
第三章旋转冲压主机设计·····································12
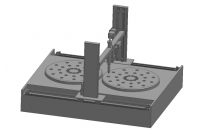
3.1旋转冲压主机的整体结构······································12
3.2旋转冲压驱动电动机的选择····································12
3.3带传动设计··················································13
3.3.1设计功率··················································13
3.3.2带型确定··················································13
3.3.3传动比····················································13
3.3.4小带轮与大带轮的基准直径··································13
3.3.5旋转液压缸实际转速········································14
3.3.6带速······················································14
3.3.7初定轴间距················································14
3.3.8带准长度··················································14
3.3.9实际轴间距················································14
3.3.10小带轮包角···············································15
3.3.11确定单根V带的基本额定功率·······························15
3.3.12额定功率增量·············································15
3.3.13确定V带的根数···········································16
3.3.14确定单根V带的预紧力·····································17
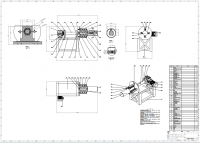
3.4零部件设计··················································17
3.4.1加紧部零件结构图··········································17
3.4.2主机机架的结构设计········································19
第四章液压站设计·············································20
4.1胀形力计算··················································20
4.2 负载计算···················································21
4.3液压系统图··················································22
4.4液压系统工作原理···········································23
4.5液压缸与夹紧液压缸的尺寸计算································24
4.5.1旋转冲压液压缸与夹紧液压缸的内径尺寸D计算················24
4.5.2旋转冲压液压缸与夹紧液压缸的活塞杆直径d尺寸计算··········25
4.5.3活塞杆最大允许计算长度····································25
4.5.4活塞有效计算长度··········································26
4.5.5最小导向长度··············································27
4.5.6导向套长度················································27
4.5.7缸筒壁厚··················································28
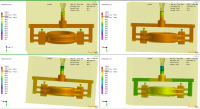
4.6旋转冲压液压缸与夹紧液压缸的强度校核························28
4.6.1活塞杆应力校核·········································28
4.6.2缸筒强度验算··············································29
4.6.3油缸稳定性验算············································30
4.7元件选型···················································33
第五章总结与展望············································34
小结与致谢···················································35
参考文献·····················································36
毕业设计附件目录············································37
参考文献
[1]张利平.液压站设计与使用.北京:海洋出版社,2004
[2]张利平等.液压气动系统设计手册.北京:机械工业出版社,1997
[3]张利平.液压传动系统及设计.北京:化学工业出版社,2005
[4]机械设计手册编委会.机械设计手册(新版)第4卷. 北京:机械工业出版社,2004
[5]成大先.机械设计手册单行本.北京:化学工业出版社,2004
[6]黄春峰.扩散管胀口模具设计.锻压技术,1999(6):18~19
[7]张利平,张玉鹏.气动胀管机的设计.制造技术与机床,1996(2): 32~33
[8]路甬祥.液压气动技术手册. 北京:机械工业出版社,2002
http://www.bysj1.com/ http://www.bysj1.com/html/1457.html http://www.bysj1.com/html/3958.html