连铸方坯动态轻压下工艺探析
摘要:连铸坯动态轻压下技术己成为改善连铸坯中心偏析和缩孔的最有效手段之一,是现代连铸机先进性的一个重要标志。本文以国内某厂的国产280mmx325mm大方坯连铸机为依托,进行了大方坯动态轻压下过程关键工艺控制模型即压下模型的研究开发,并在实际生产中进行应用研究。本文的主要研究内容和取得主要结果如下:
1.铸坯高温物性参数的测定。通过测定试验钢种的高温物性参数,为轻压下的二冷配水工艺参数的制定提供基础并为离线压下仿真过程提供精确的物性参数。测定的高温物性参数包括热膨胀、收缩系数,高温热塑性曲线,零强度温度TZST,零塑性温度场TZDT,屈服强度。
2.热收缩值是轻压下的一个重要工艺参数。通过铸坯的实时温度场分布,结合测定的高温物性参数对铸坯连铸过程进行计算,计算铸坯在整个连铸过程的热收缩量。计算结果表明:拉速对铸坯的热收缩影响较大,拉速越大热收缩量越少;过热度和钢种对铸坯自然热收缩的影响较小;热收缩速率基本相同为0.140mm/min-0.143mm/min。
3.通过对压下率理论模型的分析,结合测定的高温物性参数和大方坯的生产工艺,对铸坯实施轻压下过程进行计算,计算不同拉速、钢种下的压下率。结果表明:大方坯的压下率和压下速率均沿拉坯方向近似线性减少;平均压下率与拉速呈线性减少关系;压下速率取值范围不随拉速的变化而变化;钢种对压下率和压下速率的影响小。
关键词:大方坯;轻压下;热收缩;高温物性参数
Study on process of continuous casting billet dynamic soft reduction
Abstract: Dynamic soft reduction technology for continuous casting machine has become one of the best methods to eliminate center segregation and shrinkage cavity of as-cast semi-products, and it is an important indication of modern conticaster. Based on the domestic made 280mmx325mm bloom continuous casting machine, research of a key process control model-soft reduction model was carried. The main research Work and results are as follows:
1. Determination of the high-temperature physical parameters of bloom. By measuring the high-temperature physical parameters of trial steel, a basis for the secondary cooling water and the accurate physical parameters for the off-line reduction simulation were provided. The high-temperature physical parameters include: high-temperature thermal expansion contraction coefficient, high-temperature thermoplastic curve, TZST, TZDT, and Yield strength.
2. The simulation of the bloom natural shrinking. The shrinking volume is an important Parameter of the reduction on-line control mode. The real-time temperature field of bloom was loaded, and the thermal coupling calculation was preceded in the bloom continuous casting process with the high-temperature physical parameters. The shrinking volume of bloom was calculated during the whole CC process. The result shows that: as the casting speed increases, the shrinking volumes becomes smaller, and the casting speed has much greater effect on the bloom shrinking, while the effect of superheat and steel grade on the natural shrinking of bloom is smaller. The heat shrinking rate is basically the same as for 0.140-0.143mm/m in the withdrawal and straightening machine.
3. The simulation of the bloom reduction rate. Through analyzing thet heory model of reduction rate and being combined with the high-temperature physical parameters and the actual conditions of bloom in a factory, a finite element numerical calculation was performed for the process of bloom soft reduction, and the range and laws of reduction rate were obtained under various casting speeds and steel grades. The result shows that reduction rate and reduction gradient decrease approximately linearly along the casting strand of continuous casting bloom, and the average reduction gradient decreases linearly as the casting speed increase. The range of reduction gradient does not change with the change of casting speed, and steel grade has little effect on reduction rate and reduction gradient of continuous easting bloom.
Key Words: bloom; soft reduction; thermal shrinkage; high-temperature physical parameters.
目录
摘要.................................................................................................................................I
ABSTRACT.................................................................................................................. I
第一章 绪论................................................................................................................1
1.1 连铸技术的发展及现状.................................................................................1
1.2 大方坯连铸的中心质量问题.........................................................................3
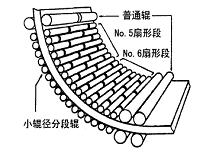
1.3 轻压下技术.....................................................................................................5
1.3.1 轻压下技术的缺点..................................................................................6
1.3.2 轻压下技术的发展..................................................................................8
1.3.3 轻压下技术的工业应用........................................................................11
1.4 本论文研究的内容及意义...........................................................................13
第二章 实验材料及方法............................................................................................14
2.1 高温物性参数测定的目的和意义...............................................................14
2.2 试样条件.......................................................................................................14
2.3 测定工艺.......................................................................................................16
2.3.1 热膨胀收缩系数的测定........................................................................16
2.3.2 热塑性曲线的测定................................................................................18
2.3.3 零强度温度的测定................................................................................18
2.4 铸坯低倍组织评级.......................................................................................19
第三章 实验结果及分析............................................................................................22
3.1 热膨胀和收缩系数.......................................................................................22
3.1.1 轴承钢GCr15.........................................................................................22
3.1.2 帘线钢72A.............................................................................................23
3.1.3 弹簧钢60SiMnA....................................................................................24
3.1.4 零强度与零塑性温度............................................................................25
3.2 热塑性曲线...................................................................................................25
3.3 高温物性参数的选用...................................................................................28
3.3.1 压下区间的选择....................................................................................28
3.3.2 收缩系数................................................................................................28
3.3.3 屈服极限................................................................................................30
3.3.4 压下率/压下量.......................................................................................30
3.4试验的铸坯偏析比结果分析........................................................................30
3.4.1铸坯厚度方向上各位置处的C元素偏析比.........................................31
3.4.2铸坯厚度方向上各位置处的Mn元素偏析比.......................................31
3.4.3铸坯厚度方向上各位置处的P元素偏析比..........................................32
4 结论..........................................................................................................................34
小结..............................................................................................................................35
参考文献......................................................................................................................37
参考文献
1.殷瑞任.中国连铸的快速发展[A],第三界发展中国家连铸会议论文集[C],2004:1-7.
2.殷瑞环,潘荫华,苏天森.中国加快连铸的途径[J],钢铁,1998,33(3):72-76.
3.蔡开科.浇注与凝固[M],北京:冶金工业出版社,1987,125-159.
4.张彩军译.板坯中心偏析形成机理及轻压下技术的改善效果[A],中国钢铁年会论文集[C],2001,624-630.
5.阎朝红.凝固末端轻压下技术在连铸中的应用[J],宝钢技术,2001,5:51-55
6.李依依,李殿中,朱苗勇.金属材料制备工艺的计算机模拟[M]北京:科学出版社,2006:70-120.
7.干勇.连续铸钢前沿技术的工程化,中国工程科学,2002,4(9):12-18.
8.王捷,杨拉道.连铸轻压下技术的最新发展[J],重型机械,2001,1:1-3.
9.王朝盈,刘彩玲,刘光辉.厚板坯连铸轻压下技术和轻压下扇形段[J],重型机械,1999,5:9-11.
10.罗秉臣,刘彩玲,王庆新.厚板坯连铸新技术[J],重型机械,1999,5:9-11.
11.林立恒译.利用轻压下法防止大方坯中心疏松技术的开发[J],冶金译丛,1996,1:34-37
12.钱静秋,智建国.连铸轻压下技术发展现状[J],钢铁,2002,10:5185-5188.
13.程乃良,陈志平.应用动态轻压下改善板坯内部质量的实践[J],炼钢,2005,5:29-32.
14.董珍译.关于高碳大方坯中心偏析的改善[J],冶金译丛,1998,1:44-48.
15.岑永权.连铸坯液芯压下工艺[J],上海金属,1997,19(5):42-48.
16.陈永.重轨钢连铸的质量控制[J],钢铁,2004,39(3):23-26.
17.朱苗勇,程乃良.连铸坯的动态轻压下技术[A],2005中国钢铁年会第三卷[C],_北京,2005:332-336.
18.朱苗勇,林启勇.连铸坯的轻压下技术.鞍钢技术,2004,1:1-6.
19.董珍编译.关于高碳大方坯中心偏析的改善 J.冶金译丛. 1998,1:44-48.
20.林启勇,蒋欢杰,朱苗勇.连铸坯动态轻压下的压下参数分析.材料与冶金学报,2004,12:261-265.
21.吴光亮,肖上工. 薄板坯连铸过程中轻压下对其组织与性能的轻压下技术影响.1996,3:15-21
http://www.bysj1.com/ http://www.bysj1.com/html/1068.html
http://www.bysj1.com/html/2068.html