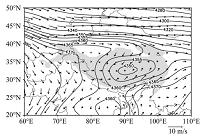
高原季风指数与中国降水的关系
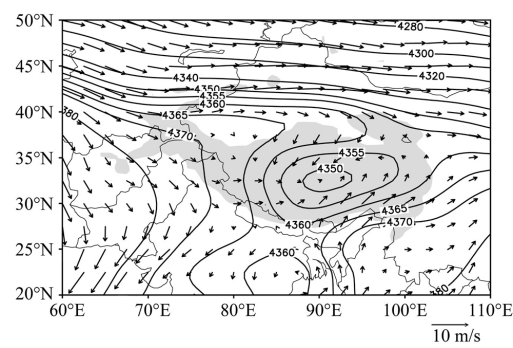
摘要:根据NCEP/NCAR、NCEP/DOE和ERA40再分析资料以及中国596个台站逐月降水观测资料,利用相关分析、小波分析和交叉谱分析等统计方法,分析了近几十年青藏高原季风变化趋势及其对中国东部降水的影响,探讨了影响高原季风长期变化的可能原因.结果表明:高原季风具有年际和年代际的多时间尺度变化特征,在1958~2010年呈显著增强趋势,同时也存在明显的年际变化.进一步分析发现,高原季风异常增强时,亚洲季风区大气环流出现显著变化,季风环流减弱,并伴随东亚季风降水异常,华南和华北降水减少,长江中下游地区降水增加.高原季风的增强趋势可能与对流层中层青藏高原—周边陆地热力差异(尤其是高原—东部平原热力差异)增大有关.
关键词: 高原季风 东亚季风 南亚季风 热力差异
The relationship between the plateau monsoon index and the precipitation in China
Abstract: Based on the NCEP/NCAR, NCEP/DOE and ERA40 reanalysis data and the monthly precipitation data from 596 stations of China, the variation of the Tibetan Plateau (TP) summer monsoon and its impact on precipitation in eastern China are investigated by using the correlation analysis, the wavelet analysis, and the cross-spectral analysis. The results show that the plateau summer monsoon exhibits the strong interannual and long-term variability. It also shows an obviously upward trend during 1958-2010. The further analysis reveals that the abnormal enhancement of the plateau summer monsoon changes the Asia atmospheric circulation and then weakens the Asian summer monsoon. This leads to an increase of monsoon rainfall over the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River and a decrease over North China and South China. The strengthening of the plateau summer monsoon over the past 50 years may be related to the enhancement of thermal difference between the TP and its surrounding plains in the middle-upper troposphere (especially of the increase of thermal difference between the TP and the plain in eastern China).
Key words: Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon East Asian summer monsoon South Asian summer monsoon thermal difference
目录
1 引言 3
2 资料和方法 5
2.1 资料 5
2.2 方法 5
3 高原季风变化及与中国降水和亚洲季风环流的关系 6
3.1 青藏高原季风的长期变化 6
3.2 高原季风与中国降水和亚洲季风环流的关系 7
4 青藏高原季风增强的可能原因 10
5 结论和讨论 14
致 谢 15
参考文献 16
参考文献
[1] 白虎志, 谢金南, 李栋梁. 2001. 近40年青藏高原季风变化的主要特征[J]. 高原气象, 20 (1): 22-27.
[2] 白虎志, 马振锋, 董文杰. 2005. 青藏高原地区季风特征及与我国气候异常的联系 [J]. 应用气象学报, 16 (4): 484-491.
[3] Chang C P, Zhang Yongsheng, Li T. 2000. Interannual and interdecadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: Roles of the subtropical ridge [J]. J. Climate, 13 (24): 4310-4325.
[4] 邓伟涛, 孙照渤, 曾刚, 等. 2009. 中国东部夏季降水型的年代际变化及其与北太平洋海温的关系 [J]. 大气科学, 33 (4): 835-846.
[5] 段安民, 吴国雄. 2003a. 7月青藏高原大气热源空间型及其与东亚大气环流和降水的相关研究 [J]. 气象学报, 61 (4): 447-456.段安民, 刘屹岷, 吴国雄. 2003. 4-6月青藏高原热状况与盛夏东亚降水和大气环流的异常 [J]. 中国科学 (D辑): 地球科学, 33 (10): 997-1004.
[6] 丁一汇, 李崇银, 何金海, 等. 2004. 南海季风试验与东亚季风 [J]. 气象学报, 62 (5): 561-586.
[7] 范可. 2006. 南半球环流异常与长江中下游夏季旱涝的关系 [J]. 地球物理学报, 49 (3): 672-679.
[8] 范可, 王会军. 2006. 有关南半球大气环流与东亚气候的关系研究的若干新进展 [J]. 大气科学, 30 (3): 402-412.
[9] 范可, 王会军. 2007. 南极涛动异常及其对冬春季北半球大气环流影响的数值模拟试验 [J]. 地球物理学报, 50 (2): 397-403.
[10] 谷德军, 梁建茵, 郑彬, 等. 2008. 华南季风降水开始日的异常与前冬大气环流和海温的关系 [J]. 大气科学, 32 (1): 155-164.
[11] 黄荣辉, 傅云飞, 臧晓云. 1996. 亚洲季风与ENSO循环的相互作用 [J]. 气候与环境研究, 1 (1): 38-54.
Huang R H. 2001. Decadal variability of the summer monsoon rainfall in East Asia and its association with the SST anomalies in the tropical Pacific [J]. CLIVAR Exchange, 6 (2): 7-8.
Kuo H L, Qian Y F. 1981. Influence of the Tibetian Plateau on cumulative and diurnal changes of weather and climate in summer [J].Mon. Wea. Rev., 109 (11): 2337-2356.
[12] 李崇银, 张利平. 1999. 南海季风活动及其影响 [J]. 大气科学, 23(3): 257-266.
[13] 李菲, 段安民. 2011. 青藏高原季风强弱变化及其对亚洲地区降水和环流的影响——2008年个例分析 [J]. 大气科学, 35 (4): 694-706. Li Fei, Duan Anmin. 2011. Variation of the Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon and its effect on the rainfall and circulation in Asia—A case study in 2008 [J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese), 35 (4): 694-706.
[14] 刘芸芸, 丁一汇. 2008. 印度季风的爆发与中国长江流域梅雨的遥相关分析 [J]. 中国科学 (D辑): 地球科学, 38 (6): 763-775. Liu Yunyun, Ding Yihui. 2008. Teleconnection between the Indian summer monsoon onset and the Meiyu over the Yangtze River valley [J]. Science in China (Series D): Earth Sciences, 51 (7): 1021-1035.
[15] 马振锋, 高文良. 2002. 热带海温变化与高原季风发展 [J]. 应用气象学报, 13 (4): 440-447. Ma Zhenfeng, Gao Wenliang. 2002. Relationship between tropical SST change and monsoon development over plateau [J]. Journal of Applied Meteorological Science (in Chinese), 13 (4): 440-447.
[16] 马振锋. 2003. 高原季风强弱对南亚高压活动的影响 [J]. 高原气象, 22 (2): 143-147. Ma Zhenfeng. 2003. Impact of strong/weak plateau summer monsoon on South Asia high activity [J]. Plateau Meteorology (in Chinese), 22 (2): 143-147.
[17] 齐冬梅, 李跃清, 白莹莹, 等. 2009. 高原季风指数的定义及其特征分析 [J]. 高原山地气象研究, 29 (4): 1-9. Qi Dongmei, Li Yueqing, Bai Yingying, et al. 2009. The definition of plateau summer monsoon index and analysis on its characteristics [J]. Plateau and Mountain Meteorology Research (in Chinese), 29 (4): 1-9.
[18] 汤懋苍, 沈志宝, 陈有虞. 1979. 高原季风的平均气候特征 [J]. 地理学报, 34 (1): 33-41. Tang Maocang, Shen Zhibao, Chen Youyu. 1979. On climatic characteristics of the Xizang Plateau monsoon [J]. Acta Geographica Sinica (in Chinese), 34 (1): 33-41.
Tang Maocang, Reiter E R. 1984. Plateau monsoons of the Northern Hemisphere: A comparison between North America and Tibet [J].Mon. Wea. Rev., 112 (4): 617-637.
[19] 汤懋苍, 梁娟, 邵明镜, 等. 1984. 高原季风年际变化的初步分析 [J]. 高原气象, 3 (3): 76-82. Tang Maocang, Liang Juan, Shao Mingjing, et al. 1984. The initial analysis on the Tibet Plateau monsoon interannual variability [J]. Plateau Meteorology (in Chinese), 3 (3): 76-82.
[20] 汤懋苍. 1993. 高原季风研究的若干进展 [J]. 高原气象, 12 (1): 95-101. Tang Maocang. 1993. Some advances on the research of plateau monsoons [J]. Plateau Meteorology (in Chinese), 12 (1): 95-101.
[21] 汤懋苍. 1995. 高原季风的年代际振荡及其原因探讨 [J]. 气象科学, 15 (4): 64-68. Tang Maocang. 1995. Discussion on inter-decade oscillation of plateau monsoon and its causes [J]. Scientia Meteorologica Sinica (in Chinese), 15 (4): 64-68.
[22] 田俊, 马振峰, 范广洲, 等. 2010. 新的高原季风指数与四川盆地夏季降水的关系 [J]. 气象科学, 30 (3): 308-135.
[23] 叶笃正, 罗四维, 朱抱真. 1957. 西藏高原及其附近的流场结构和对流层大气的热量平衡 [J]. 气象学报, 28 (2): 108-121. Ye Tucheng, Lo Szuwei, Chu Paochen. 1957. The wind structure and heat balance in the lower troposphere over Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding [J]. Acta Meteorologica Sinica (in Chinese), 28 (2): 108-121.
[24] 叶笃正, 高由禧. 1979. 高原季风现象[M]//叶笃正, 高由禧. 青藏高原气象学. 北京: 科学出版社, 62-73. Ye Duzheng, Gao Youxi. 1979. Phenomenon of Tibet Plateau monsoon [M].// Ye Duzheng, Gao Youxi. Qinghai-Xizang Plateau Meteorology (in Chinese). Beijing: Science Press, 62-63.
Yu Rucong, Wang Bin, Zhou Tianjun. 2004. Tropospheric cooling and summer monsoon weakening trend over East Asia [J].Geophys. Res. Lett., 31: L122212.
[1] 袁媛, 李崇银. 2009. 热带印度洋海温异常不同模态对南海季风爆发的可能影响 [J]. 大气科学, 33 (2): 325-336. Yuan yuan, Li Chongyin. 2009. Possible impacts of the tropical Indian Ocean SST anomaly modes on the South China Sea summer Monsoon onset [J].Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese), 33 (2): 325-336.
[25] 曾庆存, 张邦林. 1998. 大气环流的季节变化和季风 [J]. 大气科学, 22 (6): 805-813. Zeng Qingcun, Zhang Banglin. 1998. On the seasonal variation of atmospheric general circulation and the monsoon [J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese), 22 (6): 805-813.
[26] 张顺利, 陶诗言. 2001. 青藏高原积雪对亚洲季风影响的诊断及数值研究 [J]. 大气科学, 25 (3): 372-390. Zhang Shunli, Tao Shiyan. 2001. The Influences of snow cover over the Tibetan Plateau on Asian summer monsoon [J]. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences (in Chinese), 25 (3): 372-390.
Zhao Ping, Zhu Yani, Zhang Renhe. 2007. An Asian-Pacific teleconnection in summer tropospheric temperature and associated Asian climate variability [J]. Climate Dyn., 29 (2-3): 293-303.
[27] 周波涛, 崔绚, 赵平. 2008. 亚洲-太平洋涛动与西北太平洋热带气旋频数的关系 [J]. 中国科学 (D辑): 地球科学, 38 (1): 118-123. Z
http://www.bysj1.com/ http://www.bysj1.com/html/5215.html http://www.bysj1.com/html/5215.html